Do Cops Know Who to Stop? Assessing Optimizing Models of Police Behavior with a Natural Experiment
Abstract
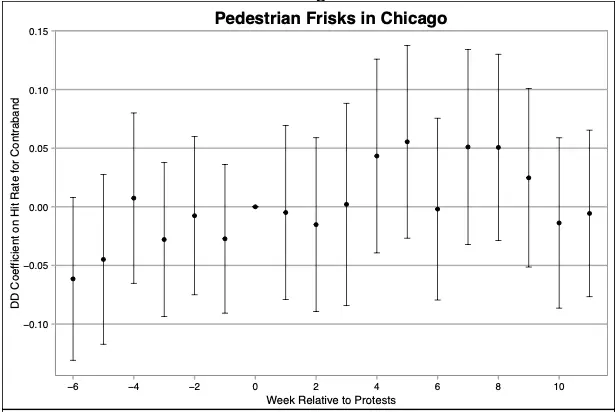
The standard economic model of police stops implies that the contraband hit rate should rise when the number of stops falls, ceteris paribus. We provide empirical corroboration of such optimizing models of police behavior by examining changes in stops and frisks around two extraordinary events of 2020 - the pandemic onset and the nationwide protests following the killing of George Floyd. We find that hit rates from pedestrian and vehicle stops generally rose as stops and frisks fell dramatically. Using detailed data, we are able to rule out a number of alternative explanations, including changes in street population, crime, police allocation, and policing intensity. We find mixed evidence about the changes in racial disparities, and evidence that police stops do not decrease crime, at least in the short run. The results are robust to a number of different specifications. Our findings provide quantitative estimates that can contribute to the important goals of improving and reforming policing.